The electronic circuit operates on DC power
All electronic devices require power supply through an AC 110V/220V voltage which is a commercial power system(or a battery) for the operation of the device. In addition, these electronic devices require stable power sources such as 3.3V, 5V, and 12V.
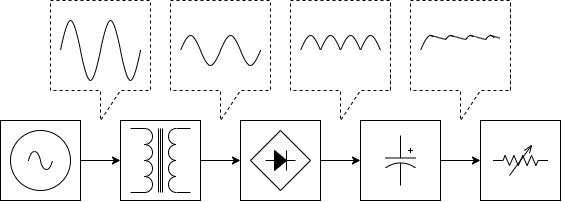
Electronic devices supplied with power through commercial power supply convert and rectified voltage to the required value by the power transformer to create a DC voltage and use it in a circuit. However, in a rectified DC power source, the performance of the device cannot be fully demonstrated because the stability and precision of the voltage are not good due to changes in the input voltage or a voltage drop of a transformer or rectifier diode.
Causes of voltage fluctuations
Quality of commercial power supply voltage
Commercial power fluctuations exist even in countries with very good power systems using sufficient costs for power plants, etc. Most of them have small fluctuations of around ±5%, but some countries under development have a very large voltage drop of more than 10-20V.
Power Transformer Voltage Drop
Although it depends on the size of the transformer, a voltage drop occurs depending on the resistance of the wire because the copper wire is wound more than hundreds of times. In addition, since the leakage inductance between the primary and secondary of the transformer is inserted in series, a voltage drop occurs.
Voltage drop in rectifier diode
Bridge diodes, which are widely used for rectification, have forward voltage drops depending on the current
Ripple Voltage
Since the AC voltage of the commercial power source is sinusoidal, ripple voltage occurs due to charging and discharging even if it is smooth with a rectifier capacitor. This is represented by voltage fluctuations of twice the frequency in the case of full-wave rectification. In addition, when a load fluctuation occurs, a larger ripple voltage fluctuation occurs due to the imbalance of charging and discharging of the rectifier capacitor.
Electronic circuits require a rated voltage
All electronic components, such as motors and relays, as well as semiconductors such as ICs, have a rated voltage that is recommended to be used and a maximum voltage that guarantees operation. Therefore, if the voltage value is exceeded, the electronic component may not operate as designed, have a shorter lifespan, or may be damaged.
For example, the rated voltage of most TTL ICs is 5V, the voltage that guarantees the operation is 4.5 to 5.5V, and the maximum voltage is 6 to 7V. In addition, in signal amplification circuits such as OPAMP, supply voltage fluctuations become signal fluctuations or noise. As a result, the designed precision or stability cannot be obtained.
As such, the fluctuation of the power voltage is a problem to be solved in terms of the performance and reliability of the device. Therefore, power stabilization and regulated power supply are required through circuit design